ˇˇ[Polymer Dispersed Liquid
Crystal (PDLC) mode]
The PDLC display consists of droplets of
liquid crystals inside a polymer network shown in figure 1. These
droplets are sized from 0.3¦Ěm to 3¦Ěm, and inside which the
molecules align themselves in a bipolar configuration.
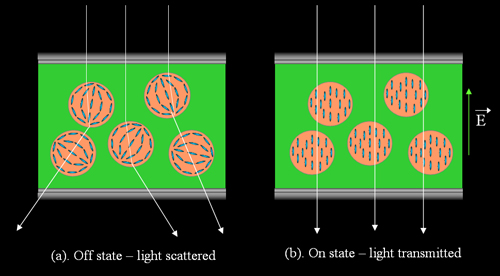
Figure 1.
Working principle of Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystal (PDLC) display
In the off state, the droplets are randomly
aligned, the refractive index n' seen by the light will be different
from np, which is the refractive index of the polymer,
hence the light is scattered or reflected in a large angle towards
the viewer. In the on state, the LC molecules orient uniformly along
the direction of the applied field, therefore the no is
the refractive index seen by the light, and usually np is
chosen as np ~ no, for this index matched
situation, light can be transmitted with a very high transmission.
Obviously, the black/off state appears milky opaque, it is a poor
black state, as a result, the contrast ratio of PDLC is relatively
low.
The formation of droplets inside the polymer
can be a micro-encapsulation process (NCAP), or a phase separation
process. In the first process, an aqueous emulsion consisting of
polymer and LC is coated on a substrate then let it dry. The second
process is a polymerization induced phase separation: the mixture is
prepared by homogeneous solution of pre-polymer LC and curing agent /
photo-initiator which catalyzes the polymerization process when the
mixture is UV irradiated. Phase separation can also be thermally
induced or solvent induced.
The working voltage and response time of the
PDLC can be affected by many factors, but mainly the resistive and
dielectric properties of LC inside the droplet and the polymer.
These properties affect the internal electric field of the droplet
which differs from the field outside the droplet. The competition
between these two field determines the final director configuration
inside the droplet, therefore, the work voltage and response time
will be present. Other factors like the size and shape of the
droplets, the viscosity of the LC etc.
There are a few factors influencing the
contrast ratio of the PDLC display. First of all is the cell gap and
the density of the droplets, they are proportional to the contrast
ratio. Secondly it is the temperature. As temperature decreases, no
decreases and ne increases, the birefringence becomes
larger, so is the scattering. As a consequence, the black/off state
is darker, so contrast ratio is higher.
Since no polarizers are not needed, high
brightness is obtained. PDLC can be used into different
applications. For example, as a light valve, PDLC can be made into a
privacy window. PDLC also find applications in project systems.
Further Readings
and References:
Fergason, J. L. "Polymer encapsulated nematic liquid
crystals for display and light control applications". SID Int. Symp.Dig.
Technol. 16, 68¨C70 (1985).
J.W. Doane, N. A. Vaz, B. G.Wu, and S. Zumer, ˇ°Field
controlled light scattering from nematic microdroplets,ˇ± Appl. Phys. Lett.,
Vol. 48, 269 (1986).
J. W. Doane, A.
Golemme, J. L. West, et al, "Polymer Dispersed Liquid Crystals for
Display Applications," Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 165, 511 (1988).
J. L. West, "Phase
Separation of Liquid Crystals in Polymers," Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 157,
427 (1988).
T. Nagata et al.,
"Silicon Chip Based Reflective PDLC Light Valve for Projection
Display", SID Symposium Digest 29, 37
(1998).
ˇˇ